- Install and use Fish Shell - fish is a smart and user-friendly command line
shell for Linux, macOS, and the rest of the family.
What’s Special About fish?

Easy to understand and use
Unlike the other shells that need a lot of setting-up to work the way you want them to, fish works perfectly right out of the box.
It ships with the most widely used features already included, which are present when you start using it without needing to install any additional plugins or tweak any configuration files unless you want to. Its syntax is simple, clean, and consistent.
Syntax highlighting
Syntax highlighting is a feature that we all wish our CLI could perform. It saves a lot of time and frustration. Well, fish does it, and it does it pretty well.
It shows you whether your command or the directory to be searched exists before you even hit enter. You’ll know whether you’re typing anything wrong before you hit enter. This makes it easier for people to parse commands, and find errors.
It highlights (most) errors in red, such as misspelled commands, misspelled options, reading from non-existing files, mismatched parenthesis and quotes, and many other common errors.
It also features highlighting of matching quotes and parenthesis. Oh, and it’s pretty, colorful.
Configuration for fish shells
The fish community maintains Oh My Fish, which is a shell framework inspired by Oh My Zsh. It offers a lot of beautiful prompt themes and awesome plugins, is lightweight, awesome, and easy to use.
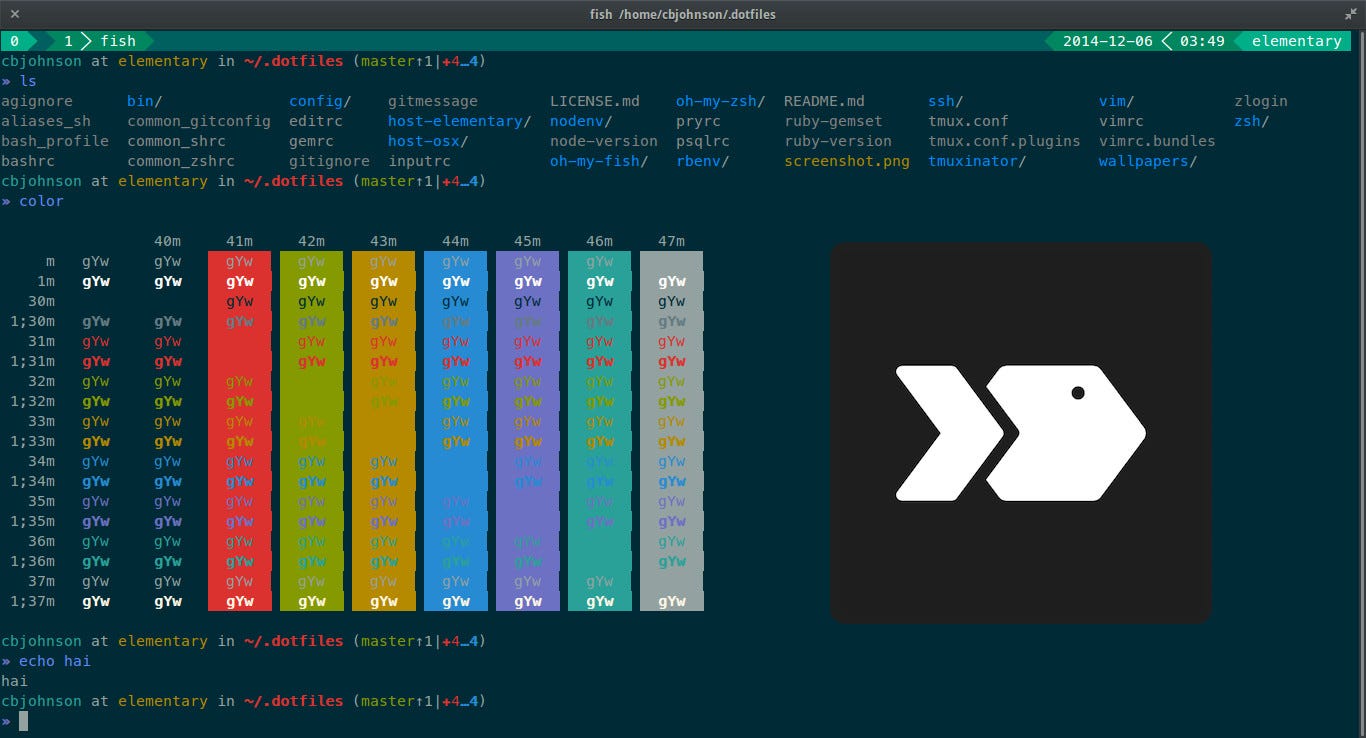
It also offers a web-based configuration feature. Just type:
fish_config
You will land on the website with which you can customize the skin of your shell.
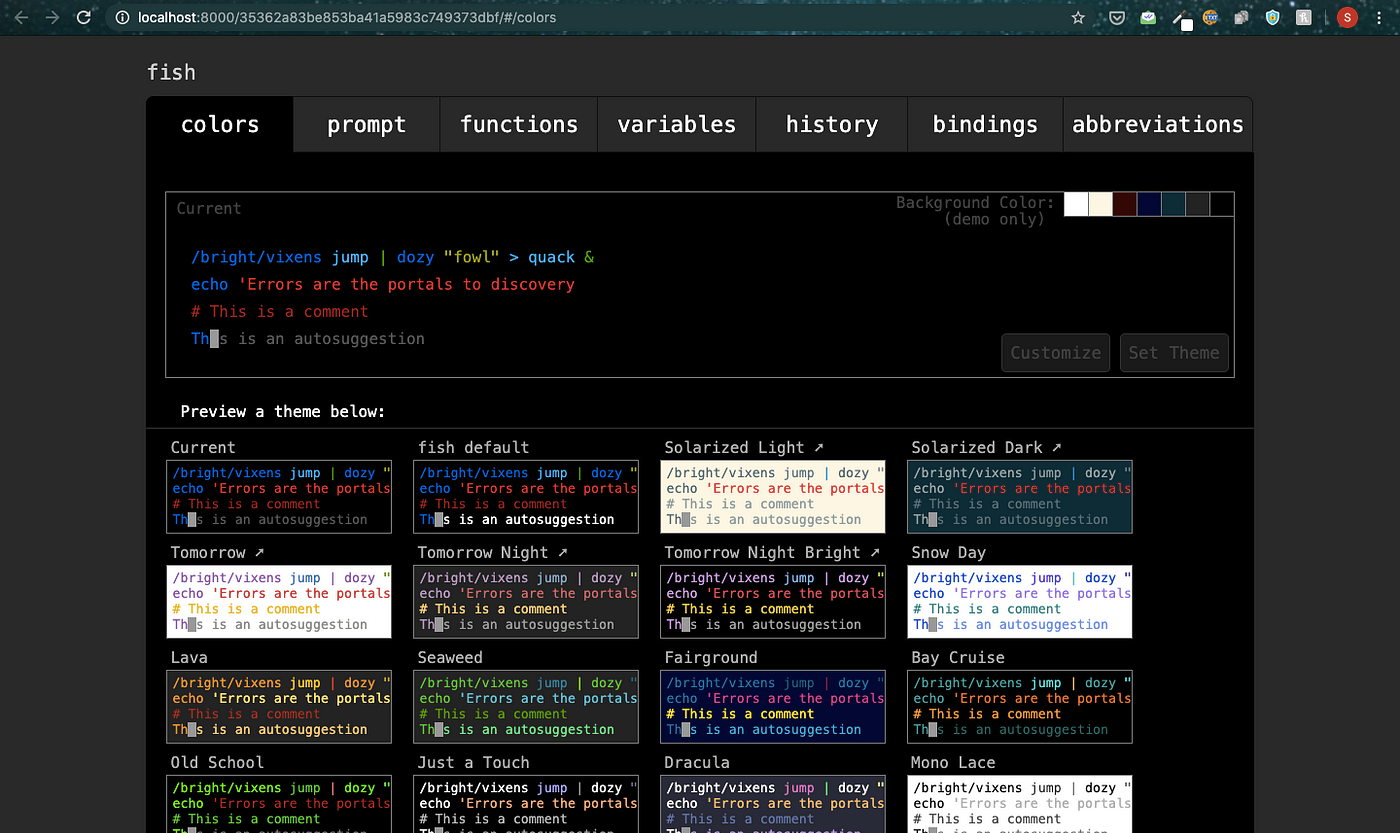
Inline searchable history
This is an interactive feature of this Shell. You begin typing a command and press the up key to see all the times in the Shell history where you used that command before.
To search the history, simply type in the search query, and press the up key. By using the up and down arrow, you can search for older and newer matches. The fish history automatically removes duplicate matches and the matching substring is highlighted.
These features make searching and reusing previous commands much faster.
Inline auto-suggestion
Fish suggests commands as you type and shows the suggestion on the right of the cursor, in grey. If you mistype a command, it will show in red to indicate that it’s an invalid command.
It also suggests the most frequently used commands and auto-completes while you type, based on your history and valid files available.
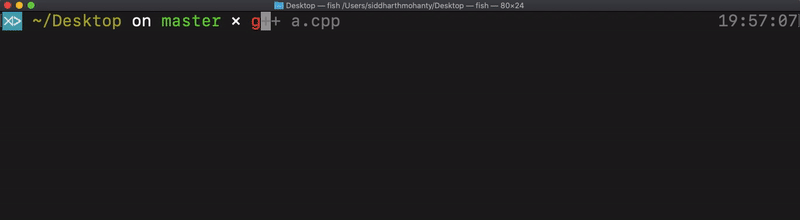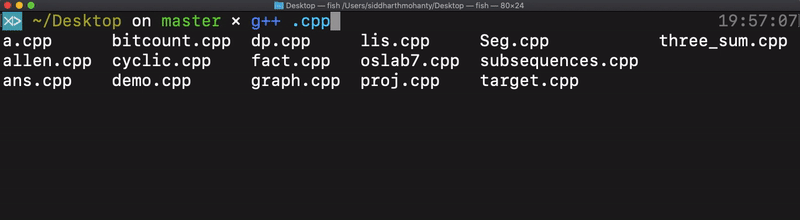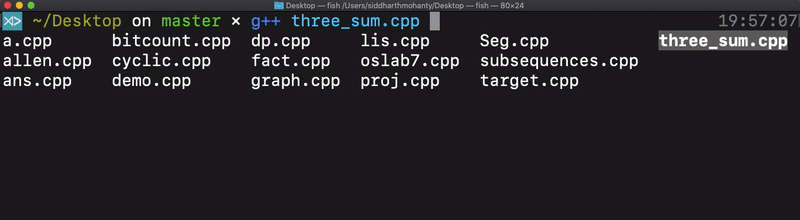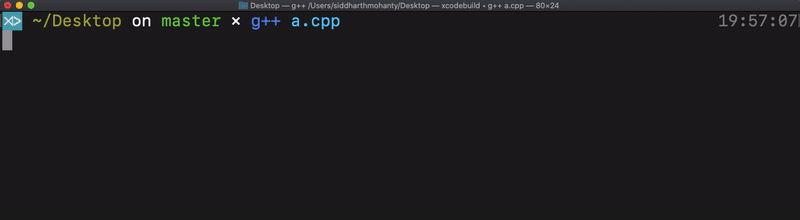
Tab completion using man page data
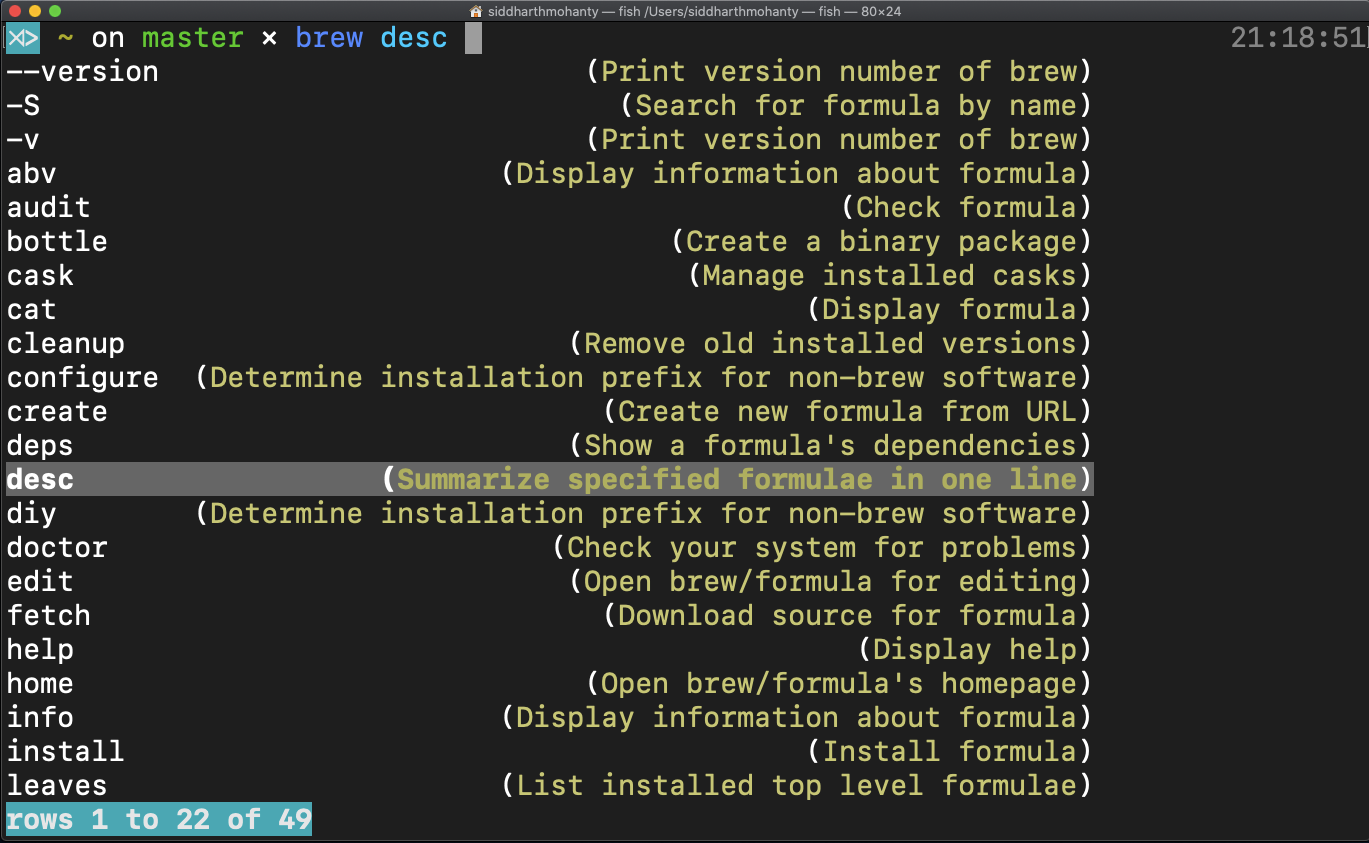
Fish can parse CLI tool man pages in various formats. Type in a command and “tab” through all the suggested auto-completions.
Steps to install and use Fish Shell
sudo apt install fish
Once the installation is completed, you can start using it by switching your current shell to Fish, for that type-
fish
Set Fish as Default shell
After using some time, if you like this colorful and friendly shell, then you can set it system default instead of bash.
chsh -s /usr/bin/fish
Log out of your system and log in again to apply the changes.
Customization
To change Fish properties, we can create a configuration file-
nano ~/.config/fish/config.fish
Switch back to Bash
If you didn’t like Fish and want back your Bash again on the terminal, then run
chsh -s /usr/bin/bash
log out and log in again.
To learn more about this shell command see the official documentation.
source: Command to Install fish shell on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS - Linux Shout