- Install CPU Power Manager.
A way to reduce energy consumption. It is about limiting the frequency of the CPU, lowering its performance. While this is something that has always been doable, it generally requires complicated terminal commands. Fortunately, there is an extension for GNOME that can help you more easily configure and manage CPU frequency. CPU Power Manager uses the frequency scaling controller intel_pstate (compatible with almost all Intel CPUs) to control and manage CPU frequency from your GNOME desktop.
General characteristics of CPU Power Manager
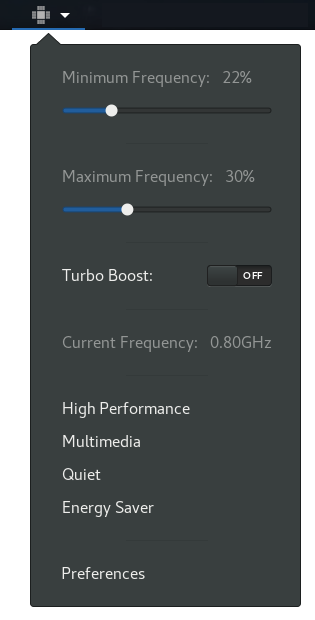
- We will be able to see the current CPU frequency. Obviously, we can use this window to see how often the CPU is running.
- Set the maximum and minimum frequency. We will be able to establish maximum and minimum frequency limits in terms of percentage. Once these limits are set, the CPU will operate only in these ranges.
- Activate and deactivate Turbo Boost. Most Intel CPUs have the 'Turbo Boost' feature. Through this, the CPU cores are increased beyond the normal maximum frequency seeking additional performance. While this can make the system more efficient, it also greatly increases energy consumption. Therefore, if we need to do anything intensively, it is good to be able to deactivate Turbo Boost and save energy.
- We will be able create profiles with a maximum and minimum frequency. These can be easily activated or deactivated, instead of touching the values.
Read more at CPU Power Manager, controls and manages the CPU frequency | Ubunlog
15 ...